In the era of 5G communication, the way 5G services are deployed has fundamentally changed and securing the 5G infra and services is of paramount importance.
5G is no longer a user and operator communication only, its about VR,AR,MR, EMBB(enhanced mobile broadband), MMTC(massive machine type communication)and URLLC( ultra-reliable and low latency communication) much more.
Also one more hurdle to the task it shifts of telecom world into the IT space, where we are no longer talking about physical or traditional VM based core application running on proprietary telecom protocols. Now the fundamental shift is to VNF, container based application, even the protocols RESTful API based on service based architecture. This is where 5G deployment wherein we use the existing upgraded 4G radio and the core. This mainly caters to high speed and just puts the telecom provider in the 5G map. However, for the URLLC and MMTC use cases telecom operator has to move to the SA version of 5G.
Before we begin into the real security issues, lets have a look at basics of 5G.
The spectrum

Deployment models
- NSA – Non stand alone
- SA – Standalone
The architecture
From traditional tin based hardware to truly cloud native application, from boxes its now functions, from proprietary telecom protocols to standard REST API. A solution that truly is cloudification, if utilized to the true potential.
From dedicated interface cards to micro services, where each micro service serves a specific business purpose and built by a specific team. Even the applications are containerized and in the real sense support business.

Basic building blocs of 5G from radio to the core
- UE talks to RAN , in 5g this is called AN (access network) This can include 3GPP and no 3GPP components – GnodeB[RS2] , wifi
- UE then connect to AMF (access mobility function)
- Other core elements the UE connect to are session management function
- Policy control function
- Application function
- Authentication server function
- User plane function
- User data management
- Network slice selection function
AS the function names have totally changed, lets drive an analogy between the LTE and 5G nodes
| 4G/3G/2G Node | Corresponding 5G Node |
| HSS, HLR | Unified data management(UDM) |
| HSS, HLR | Authentication server function(AUSF) |
| HSS, HLR | Unstructured data user function (UDSF) |
| This component does not exist in earlier generation as defined by 3gpp | Network repository function(NRF) |
| HSS, HLR | Unified data repository(UDR) |
| This component does not exist in earlier generation as defined by 3gpp | Network exposure function (NEF) |
| This component does not exist in earlier generation as defined by 3gpp | Network slice selection function(NSSF) |
| EIR | EIR |
| DRA/DEA | Service communication proxy(SCP) |
| DRA/DEA | Service edge protection proxy(SEPP) |
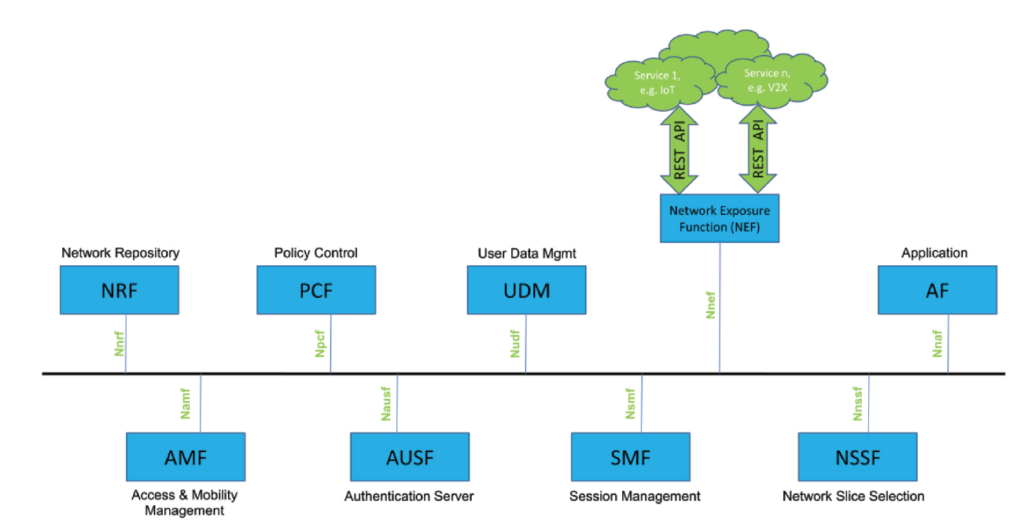
Different types of API’s in 5G – SBA, make use of different URI, HTTP, data description languages,
- Northbound API’s
- Orchestration API’s
- Internal API’s
Example RESTful SBA Procedures
Example 1: User wants to surf internet
UE calls the AMF
AMF call the NRF
NRF calls the SMF
UE contacts the SMF

In the above its clearly observed that the request above are HTTP POST request and response. The security issues that are faced by HTTP post are now inherited with this SBA in 5G.
Example 2 : Service registration
SMF send request to NRF
SMF send HTTP PUT request to NRF.

This is how the API’s from operator side shall be exposed to the 3rd parties for their application consumptionS
Security issues in API / HTTP 2.0 usage in 5G
The HTTP methods on which 5G SBA has extreme reliance are the following
HTTP POST – used to create new resource which can be addressed by the URI
The HTTP post method is mostly used now a days to impact availability of the system in form of denial of service. Potentially exploiting the confidentiality as the HTTP POST request is clear text and not encrypted
HTTP GET – request for list/ retrieves the resources addressed by URI
HTTP PUT – request replaces the resourced addressed in URI
HTTP DELETE – request deleted the resource addressed in the URI
HTTP PUT and DELETE are used by an attacker this method which was originally used for file management operations is used to change or delete files from the server’s file system, arbitrarily. For sure, if these are enabled, it opens you to some dangerous attacks and you increase your attack surface.
Some critical interfaces and their security concerns
NG1,NG2,NG3 – all are potential candidates of REST API communication. Hence this leads the way for service based architecture …
- N6 –
- N8-
- N12-
- Nnef –
Security Issues
The security issues really are ranging from identity theft, to availability disruption to life saving services, non repudiation, API security issues, container security issues during the runtime, docker/kubernetics related security issues, privacy, SSL certificate related issues. The attack surface for 5G is really huge. Job of a security team is key over here. To understand about all issues and to put any type of security control over here will really needs in depth understanding of the 5G (NSA or SA) landscape.
In this article we just discuss about only one issues specific to API’s, as its something new to the Telco work from a core services point of view.
Articles about other security issues will soon follow.
http://slkjfdf.net/ – Owofexice Ojicxq qzx.jlnn.cybersecinfinity.in.xev.td http://slkjfdf.net/