5G AKA authentication process – (3GPP 33501)
Hello my readers today we will talk about two ways to authenticate a UE in 5G :-
5G AKA (Authentication Key Agreement)
EAP AKA
The below components in the 5G network architecture are instrumental in the authentication process

UE – User equipment
SEAF – Security anchor function
AUSF – Authentication server function
UDM – Unified data management
You can consider AUSF as the MME/MSC and UDM as HSS / HLR of the older generation of 3GPP
Here is the step vise authentication process for the UE to the network and vice versa :-
- On the N1 interface UE send {N1 message with SUCI (if attach for 1st time) else 5G GUTI}

Quick recap on the permanent and temporary identifier used during the attach request and subsequent network usage
| 2G,3G | 4G,5G | Type of subscriber identifier | When is this used |
| IMSI Internation mobile subscriber identity | SUPI Subscriber permanent identity | Permanent | In order to avoid MITM, only during exceptional scenarios of first time attach Or When the network is unable to resolve SUPI from SUCI/GUTI |
| TMSI Temparory mobile subscriber identity | GUTI Global unique temparory identifier | Temporary | Each time location is updated or attach attempt is made or call is attempted or as set in the PLMN parameters |



HEAV – Home environment authentication vector

AV – Authentication vector



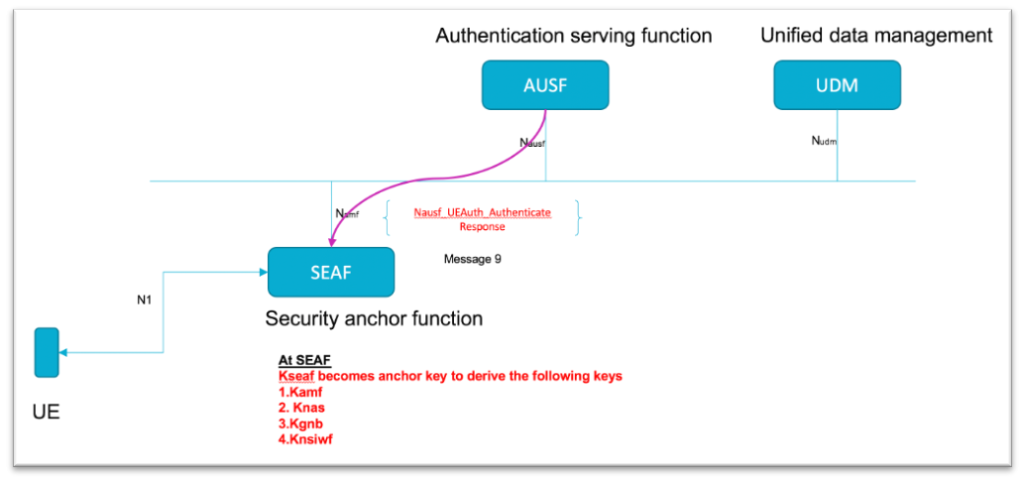
As you can see now the required keys for session to continue are derived for a session
Kseaf becomes the anchor key to derive Kamf, Knas, Kgnb,Knsiwf
Here the subscriber is successfully authenticated, serving network has been authenticated and the home network has been authenticated. This is the change from earlier generation and added layers of authentication have been added to safeguard the consumer
Do share you comments and let me know, was the article information and definitely i do welcome your comments to further improve the blog…… happy reading

One thought on “5G AKA authentication process – (3GPP 33501)”